The IT landscapes are becoming increasingly complex. Businesses are rapidly adding more applications to their tools and technology stack. This shift is creating a pressing need for seamless connectivity between these applications and making integration platforms absolutely indispensable.
The global iPaaS market size is projected to grow to USD 78.28 billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 25.3% during the forecast period. This growth is driven by the increasing need for efficient and seamless integration of disparate systems.
Integration can be achieved through two primary methods: pre-packaged integrations and custom integrations. Each has its own advantages and challenges, making it crucial to understand which is best suited for your business needs. This blog is aimed at helping you make that decision.
What is pre-packaged integration?
Pre-packaged integrations are ready-made solutions that seamlessly integrate specific applications with your existing systems. These integrations are designed to handle standard processes and functionalities directly from the vendor, making them quick and easy to implement.
Key features
- Pre-built connectors: Ready-to-use connectors for popular applications, ensuring quick and seamless integration.
- Ease of use: Designed to be user-friendly, requiring minimal technical expertise to implement.
- Standard integration: Consistent and reliable integration processes across different applications, ensuring compatibility and reducing errors.
- No-code/Low-code implementation: Often support no-code or low-code implementation, allowing non-technical users (citizen developers) to set up integrations without extensive coding knowledge.
Benefits
- Rapid deployment: Pre-configured to meet specific requirements, these integrations enable quick implementation, often within days or weeks.
- Cost-effectiveness: Saves time and resources by reducing the need for extensive development efforts and ongoing maintenance.
- User-friendliness: Designed for non-technical users, these integrations require minimal technical knowledge, making them accessible to a broader audience.
- Continuous updates: Vendors provide regular updates, ensuring the integration remains current with new features and security patches, thus maintaining system security and functionality.
- Scalability: Can scale with your business needs, accommodating growth and changes without significant additional investments.
Challenges
- Limited customization: These integrations may not cover all specific business needs, leading to functionality gaps that require additional solutions or workarounds.
- Redundant features: Some pre-built functionalities may not be relevant to your business, potentially complicating the workflow and adding unnecessary complexity.
- Dependency on the vendor: Reliance on the vendor for updates and support can limit flexibility and responsiveness to emerging business needs or issues.
What is custom integration?
Custom integrations involve building tailored solutions to connect applications that do not have native compatibility. These integrations require more time and technical expertise but offer greater flexibility and precision.
Key features
- Tailored solutions: Custom-built to meet specific business requirements, ensuring precise alignment with unique workflows and processes.
- Flexibility: Can adapt to changing business needs and integrate diverse applications, including legacy systems and new technologies.
- Advanced functionalities: Supports complex integrations and bespoke functionalities that pre-packaged solutions cannot offer.
- Scalability: Designed to scale with the evolving needs of the business, ensuring long-term viability and adaptability.
Benefits
- Enhanced efficiency: Custom solutions can streamline operations by integrating unique business processes, reducing manual work, and improving overall efficiency.
- Cost savings: While initial costs may be higher, custom integrations can save money in the long run by reducing the need for multiple workaround solutions and ongoing patchwork.
- Productivity: Tailored integrations can improve productivity by ensuring seamless workflows, reducing downtime, and minimizing errors.
Challenges
- Time-consuming: Developing custom integrations takes significantly longer than deploying pre-packaged solutions, often requiring months of development and testing.
- Higher costs: Initial development and ongoing maintenance require dedicated resources, which make them more expensive in the short and long term.
- Require technical expertise: A skilled technical team is necessary to develop, implement, and maintain custom integrations, which can be a barrier for smaller businesses without in-house expertise.
- Require maintenance: Continuous maintenance and updates are required to keep the integration functional and secure, adding to long-term costs and resource needs.
When does pre-packaged integration work best?
- Standard integration needs: Small and medium businesses often use widely adopted applications like Salesforce, Shopify, and QuickBooks. These platforms commonly offer pre-built connectors that facilitate easy integration with other tools.
- Limited IT and technical resources: Smaller businesses typically do not have large IT departments. Pre-packaged integrations enable these companies to seamlessly integrate without needing extensive technical support or development time.
- Cost-effectiveness: Businesses with limited budgets benefit from the lower upfront costs associated with pre-packaged solutions, avoiding the significant expense of custom development.
- Rapid deployment needs: Businesses undergoing mergers, acquisitions, or rapid expansion need quick integration solutions to maintain operational continuity. Pre-packaged integrations can be deployed swiftly, minimizing downtime and disruption.
When does custom integration work best?
- Complex Workflows: Large enterprises often have intricate, multi-layered workflows that require tailored solutions to integrate diverse and legacy systems seamlessly.
- Global Operations: With operations across different regions, large businesses need integrations that can handle varying regulations, languages, and operational practices, which custom solutions can provide.
- Unique Requirements: Businesses with highly specialized processes, such as custom manufacturing or specialized financial services, need integrations that can accommodate their unique workflows and data requirements.
- Competitive Advantage: Custom integrations can provide a competitive edge by enabling proprietary processes and innovations that standard solutions cannot offer.
- Advanced data handling: Companies needing precise data transformation, such as converting data formats (e.g., XML to JSON) or complex data enrichment, benefit from custom integrations.
- Security and Compliance: Industries with strict regulatory requirements, like healthcare and finance, require custom integrations to ensure compliance with standards like HIPAA or GDPR, offering tailored security measures and audit trails.
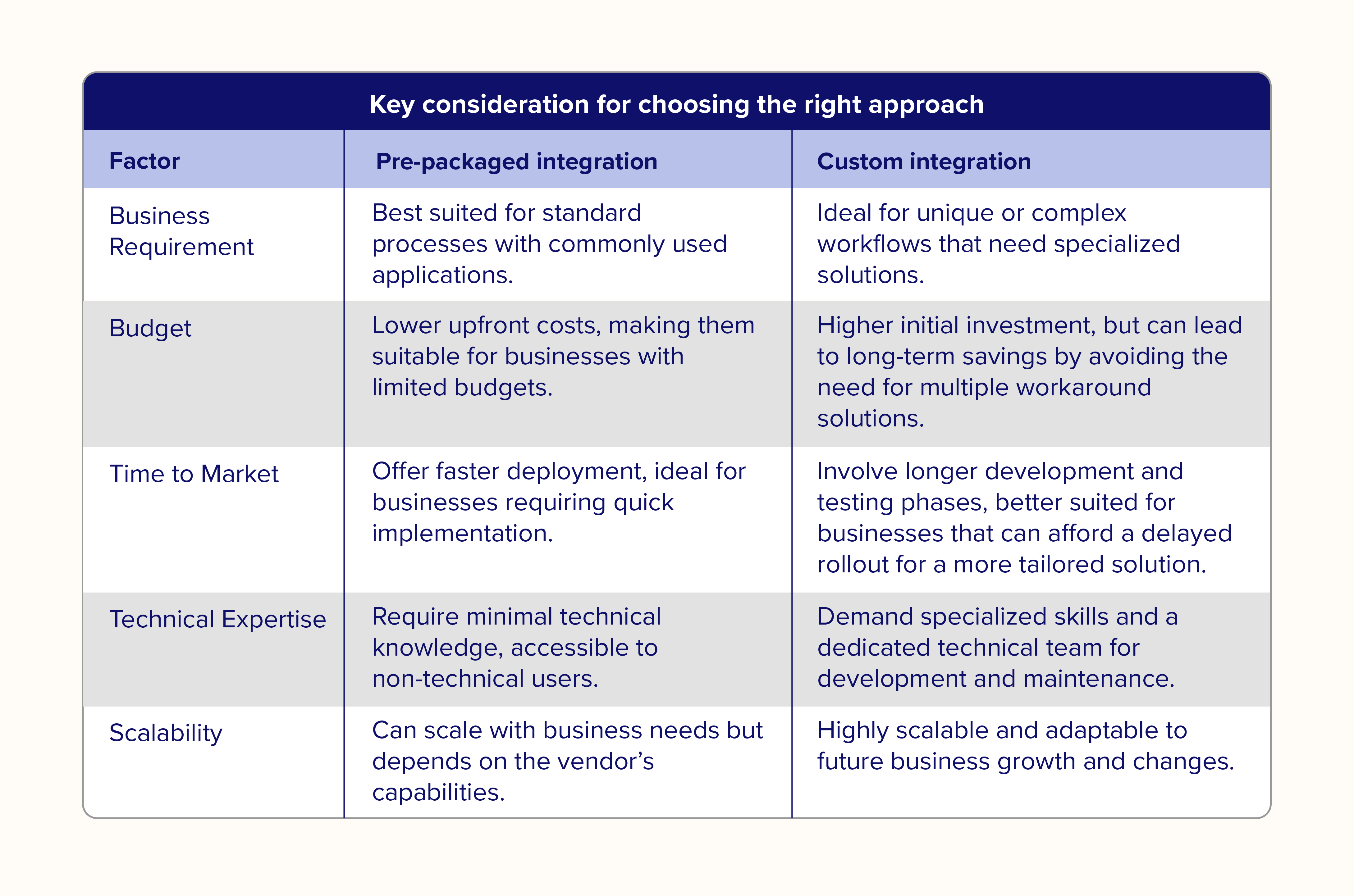
Key considerations for choosing the right approach
When deciding between pre-packaged and custom integrations, consider the following factors:
Related read: Embedded iPaaS - Why do you need it?
Conclusion
Choosing between pre-packaged and custom integrations depends on your business needs, budget, and technical capabilities. Both approaches have their advantages and challenges. An embedded Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) like Quickwork offers the best of both worlds, providing pre-built connectors for immediate deployment and tools for developing custom integrations to meet specific requirements.
Quickwork’s scalable solution requires minimal technical knowledge, thanks to its no-code integration and automation capabilities. Whether you need pre-packaged or custom integrations, Quickwork can help streamline your workflows efficiently. To know more about us, write to sales@quickwork.co.








