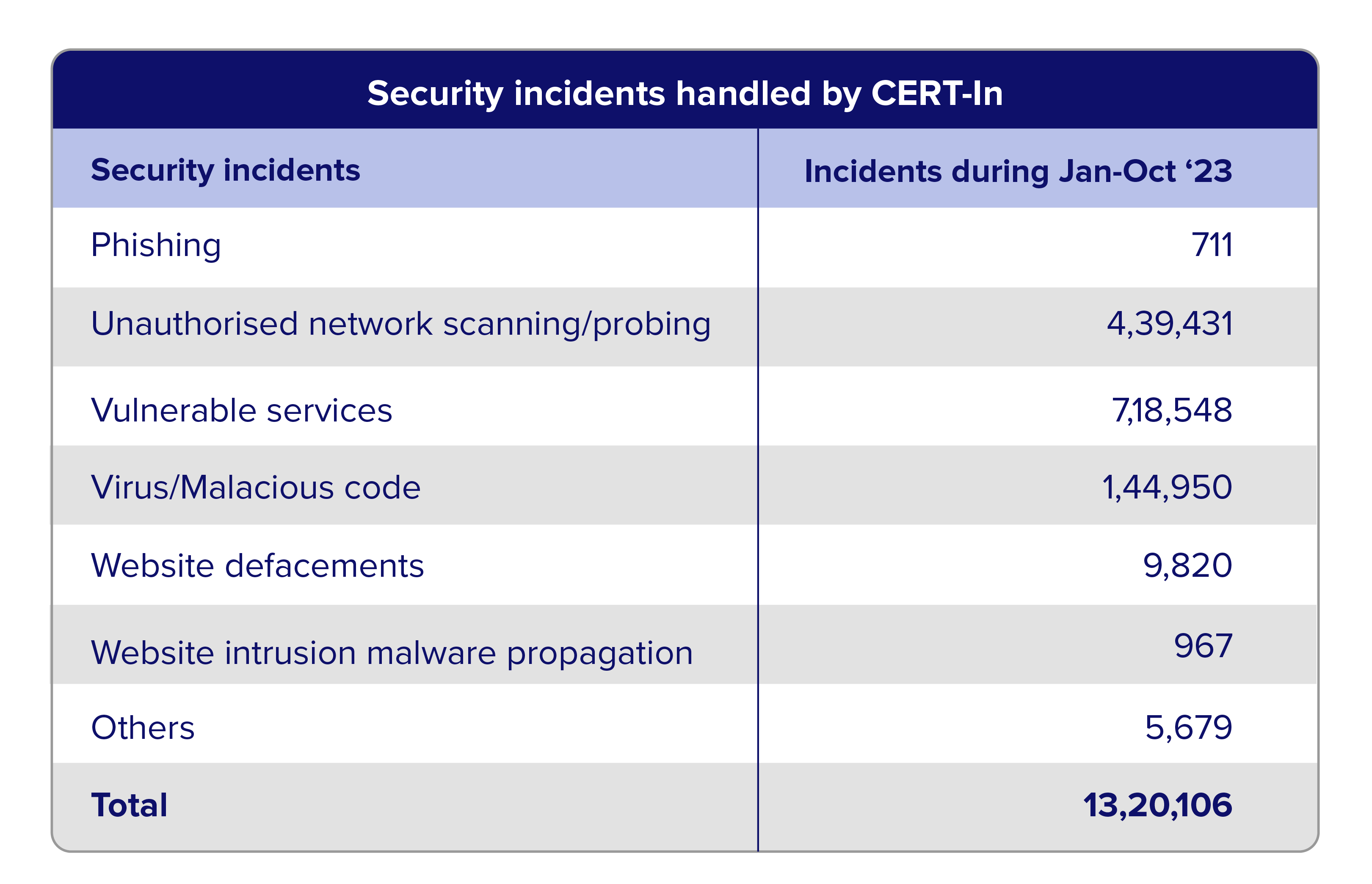
The digital transformation of India's financial services sector is reshaping how institutions operate, offering unprecedented efficiency and improved customer experiences. However, as banks and financial organizations increasingly depend on digital technologies, the risk of cyber threats also escalates. According to a report from the RBI, the Indian financial sector faced more than 13 lakh cyber-attacks during Jan-Oct 2023.
Advanced integration solutions are at the forefront of addressing these security challenges. By streamlining the flow of information between disparate systems, these platforms not only enhance operational efficiencies but also strengthen the cybersecurity framework of financial institutions. They ensure that as systems become more interconnected, they remain secure against potential breaches.
Cybersecurity threats targeting financial services
Financial institutions in India have faced a rising tide of cyber attacks characterized by their sophistication and diversity. These attacks not only aim to steal valuable financial data but also to disrupt the operations of financial institutions, underscoring the urgent need for robust cybersecurity measures. Here are some latest types of cyber attacks:
- Ransomware attacks: are those threats in which attackers encrypt an institution's data and demand payment for its decryption. These cause operational disruptions and financial losses; demands for ransom can be exorbitantly high.
- Phishing scams: are fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details by disguising as a trustworthy entity in electronic communications. They lead to unauthorized access to financial accounts and can result in significant financial theft.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): are continuous and stealthy cyber hacking processes aimed at gaining access to the system and remaining inside for a prolonged period without being detected. These often target critical data and infrastructure for espionage or data theft, posing long-term security risks.
- Spear Phishing: is a more sophisticated form of phishing that targets specific individuals or organizations with tailored and convincing messages. These attacks increase the likelihood of successful breaches, as personalized attacks are often harder to detect and can bypass standard security measures.
Where financial systems fall short
The surge in cyber attacks on financial institutions in India can be attributed to several key factors, forming a complex web of vulnerabilities:
- Rapid digitalization: The swift shift towards digital financial solutions and online services has expanded financial institutions' digital footprints, making them more susceptible to cyber-attacks.
- Inadequate security measures: Many financial organizations (traditional banks) still operate with outdated security infrastructures or fail to implement rigorous cybersecurity protocols, leaving critical gaps that cybercriminals exploit.
- Growing sophistication of cybercriminals: Attackers are continuously advancing their methods and technologies, using more sophisticated techniques to bypass traditional security measures. This includes malware, ransomware, and social engineering tactics tailored to deceive and infiltrate banking systems.
- Regulatory and compliance challenges: Compliance with evolving cybersecurity regulations can be inconsistent, and lapses create opportunities for cyber threats to take hold.
Together, these factors contribute to a heightened risk environment for cyber attacks within India’s financial sector, underscoring the need for enhanced security practices and robust digital infrastructures.
How do integration solutions strengthen cybersecurity in financial institutions
Integration platforms significantly enhance the cybersecurity posture of financial institutions by managing data flows and enforcing robust security protocols efficiently. These platforms provide a comprehensive solution to various security needs through integrated, advanced features:
- Centralized security management
By offering a unified view of all data exchanges within the institution, integration platforms simplify the monitoring, management, and securing of data flows. This centralized approach enhances the institution's capability to detect and respond quickly to anomalies and potential security breaches, thereby reducing the risk of significant data loss. - Advanced data protection
Integration platforms safeguard sensitive data by employing high-level encryption for data both in transit and at rest. They also enforce strict access controls, restricting data access exclusively to authorized personnel, which minimizes the chances of internal and external data breaches. - Data access control
Integration platforms use Multi Factor Authentication (MFA) that adds a crucial layer of security, requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification to access systems, networks, or data. This method significantly lowers the risk of unauthorized access by combining something the user knows, something the user has, and sometimes something the user is, such as a fingerprint or other biometric data. - Compliance and regulation adherence
Integration platforms automate compliance processes to help financial institutions meet stringent data protection and privacy regulations. They support adherence to standards like ISO 27001 and GDPR, ensuring systematic risk assessments and the implementation of necessary security controls. Detailed logs and audit trails generated by these platforms facilitate compliance audits and investigations into security incidents. - Real-time threat detection and response
Equipped with threat intelligence tools, these platforms can analyze and identify potential threats in real time. They are capable of initiating predefined security protocols automatically upon detecting suspicious activities, effectively preventing breaches before they escalate. - Regular security updates
Providers continuously develop and deploy updates and patches to safeguard against new vulnerabilities and emerging threats. These updates are essential for maintaining the integrity of the system against the latest cyber threats, including zero-day exploits and APTs. - Scalability and future-proofing
As financial institutions grow and their data needs evolve, integration platforms can scale accordingly to handle increased data volumes without compromising security. They are designed to integrate new security technologies as they become available, ensuring that the institution’s defenses remain cutting-edge.
By integrating these features, modern integration platforms provide robust defenses that help financial institutions effectively manage and mitigate risks associated with cyber threats. This comprehensive approach not only ensures the security and privacy of sensitive data but also supports the institution's resilience against the complexities of the evolving digital landscape.
Cybersecurity innovations on the horizon
As the digital landscape evolves, so too does the field of cybersecurity, with continuous innovations aimed at staying ahead of potential threats. Financial institutions, in particular, can look forward to leveraging cutting-edge technologies in integration platforms that enhance their defense mechanisms significantly:
- Predictive cybersecurity measures
Future integration platforms are expected to be equipped with AI capabilities that enable predictive cybersecurity. These advanced systems will analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential security incidents before they occur. By integrating AI and machine learning algorithms, these platforms will provide proactive security measures, alerting institutions to vulnerabilities and potential threats in real time. - Enhanced encryption techniques
Cyber threats continue to rise, making sophisticated countermeasures necessary. Upcoming advancements in encryption technology are poised to include quantum cryptography, which promises a new level of data protection that is theoretically impervious to traditional decryption methods, even by quantum computers. This form of encryption utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to secure data, providing a foolproof method of protecting information transmitted over networks. As quantum computing becomes more accessible, quantum cryptography will play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive financial data against the most advanced cyber threats. - Integration of Blockchain technology
Another significant innovation on the horizon is the integration of blockchain technology within cybersecurity frameworks. Blockchain's decentralized nature makes it an excellent tool for enhancing data integrity and transparency in financial transactions. By recording data in a tamper-evident, distributed ledger, blockchain technology can prevent fraud and unauthorized data alterations, making it an invaluable asset for financial institutions seeking to enhance their cybersecurity measures.
Related read: Blockchain APIs: The future of secure financial transactions in India
- Adaptive security architecture
The future of cybersecurity in financial services is also expected to move towards more adaptive security architectures. These systems are designed to dynamically adapt to the changing security landscape, automatically adjusting security protocols based on current activity and potential threats. This approach ensures that security measures are always aligned with the level of risk, providing robust protection tailored to real-time conditions.
These forward-thinking cybersecurity innovations aim to shield against current threats and are designed to adapt and evolve in response to emerging challenges, ensuring that financial institutions can maintain a high level of security as digital technologies advance.
Conclusion
As the Indian financial services sector rapidly evolves, so too must our approach to cybersecurity. The integration of advanced security measures through modern platforms is essential, but equally important is the cultivation of widespread cybersecurity awareness. By educating all levels of personnel on the latest cyber threats and best practices, financial institutions can build a proactive defense culture. This dual approach of leveraging cutting-edge technology alongside comprehensive training and awareness programs ensures robust protection against cyber threats, maintaining the integrity and trust of India's financial services industry.








